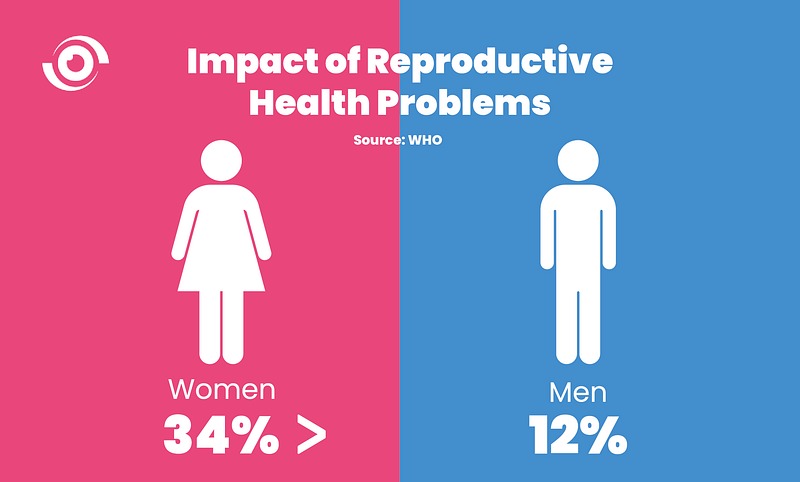
When we talk about reproductive health, conversations often center on women. However, several serious conditions can affect both men and women, and recognizing the signs early can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. Reproductive system disorders are not only uncomfortable—they can impact fertility, long-term health, and even increase the risk of certain cancers if left untreated.
This article takes a closer look at some of the most dangerous gynecological and urological conditions that can affect both genders, backed by insights from the World Health Organization (WHO), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and Mayo Clinic. We also offer practical prevention tips and treatment options to protect your health.
Why Reproductive Health Awareness Matters

The reproductive system is a complex network of organs and hormones that play key roles in sexual health, fertility, and hormone regulation. When this system is compromised, it can lead to pain, infection, infertility, or more serious health risks like chronic illness and cancer.
Unfortunately, many people are unaware of the early symptoms of reproductive disorders. Some may ignore signs due to embarrassment, while others delay seeking medical help due to stigma. Early detection and education are key to prevention and successful treatment.
Common and Dangerous Reproductive Health Conditions in Men and Women
1. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
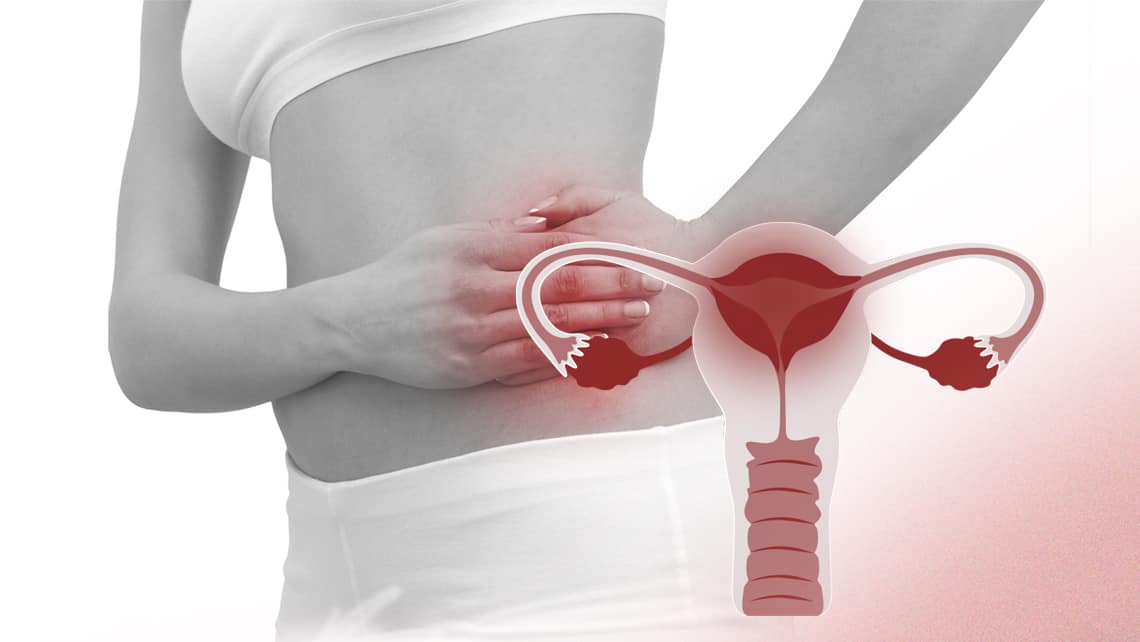
Affects: Primarily women, but men can be carriers of the infection that causes it.
What it is: PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs, often caused by untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as chlamydia or gonorrhea. If untreated, it can lead to permanent damage to the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, increasing the risk of infertility and ectopic pregnancy.
Men’s role: Men may not show symptoms of STIs but can unknowingly transmit infections to partners. This makes regular testing and safe practices critical for both sexes.
2. Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Affects: Both men and women.
What it is: HPV is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections in the world. While many cases resolve on their own, some strains of the virus can lead to cervical cancer in women, penile cancer in men, and throat or anal cancer in both sexes.
Prevention: The HPV vaccine is highly effective in preventing the strains most likely to cause cancer. The CDC recommends vaccination for both boys and girls, ideally before sexual activity begins.
3. Genital Herpes
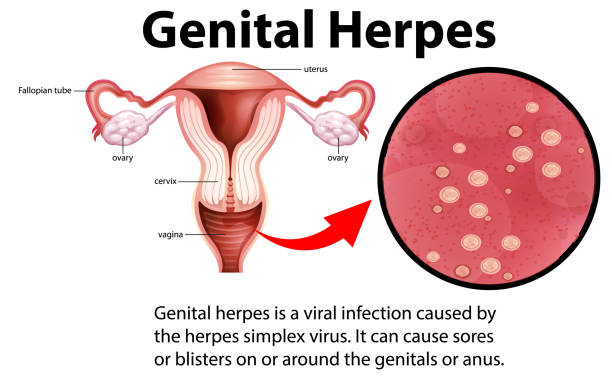
Affects: Both men and women.
What it is: Caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), genital herpes is a lifelong condition with periodic outbreaks. While not life-threatening, the virus can cause painful sores, emotional distress, and, in rare cases, complications during pregnancy.
Note: Many people with HSV don’t show symptoms but can still transmit the virus. Safe practices and open communication with partners are essential.
4. Endometriosis (in women) and Chronic Prostatitis (in men)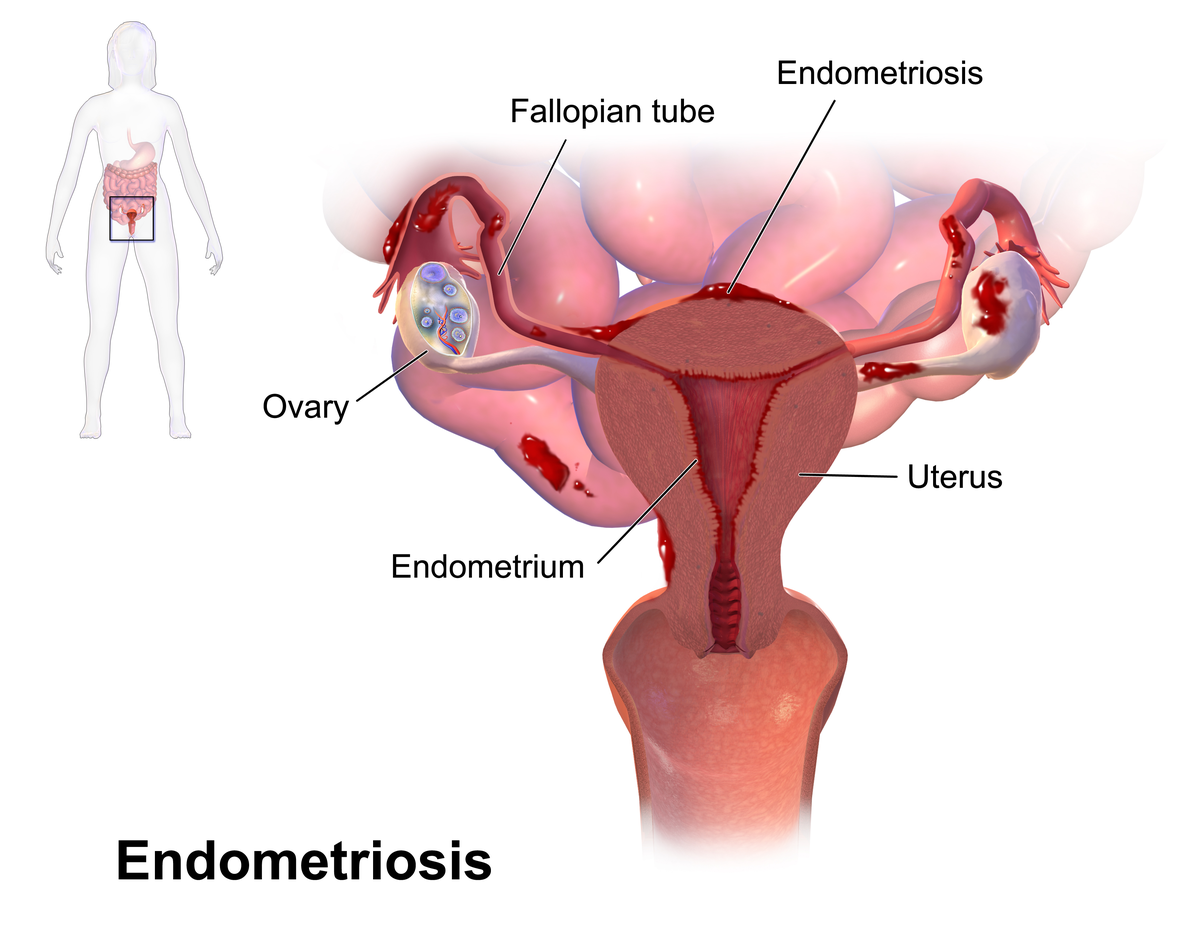

Though these conditions are gender-specific, both share similar symptoms like pelvic pain, discomfort during urination, and impacts on sexual health.
-
Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, leading to inflammation, pain, and fertility problems.
-
Chronic prostatitis involves inflammation of the prostate gland, often causing pelvic pain and urinary symptoms in men.
Management: These conditions may require lifestyle changes, pain management, physical therapy, or hormone treatments. Early diagnosis improves quality of life.
5. Infertility
Affects: Both men and women.
According to the World Health Organization, infertility affects roughly 1 in 6 couples globally, and both male and female factors contribute. Causes can include hormonal imbalances, structural problems, lifestyle factors (such as smoking or poor diet), or untreated infections.
Diagnosis and Treatment: Fertility testing for both partners is essential. Treatments range from medication to assisted reproductive technologies like IVF.
Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore

Recognizing the early warning signs of reproductive health issues can lead to timely intervention. Watch out for:
-
Persistent pelvic or lower abdominal pain
-
Unusual discharge or odor
-
Painful urination or intercourse
-
Irregular menstrual cycles (for women)
-
Erectile dysfunction or testicular pain (for men)
-
Chronic fatigue and low libido
-
Fever with pelvic discomfort
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention promptly.
Prevention Tips for Better Reproductive Health
-
Practice Safe Intimacy
-
Use barrier protection (e.g., condoms) to reduce the risk of STIs.
-
Get tested regularly if sexually active with new or multiple partners.
-
-
Get Vaccinated
-
The HPV vaccine is crucial for preventing certain cancers and is recommended for both boys and girls aged 9–26.
-
-
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
-
Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking or excessive alcohol consumption.
-
-
Manage Stress
-
Chronic stress can impact hormonal balance and reproductive function. Incorporate relaxation techniques into your routine.
-
-
Schedule Regular Checkups
-
Annual physicals and gynecological or urological exams are essential for early detection of issues.
-
-
Communicate With Your Partner
-
Open discussions about sexual health and wellness foster mutual trust and prevent misunderstandings.
-
Treatment and Support Options
Treatment for reproductive health conditions varies based on the diagnosis but often includes:
-
Antibiotics for infections
-
Hormonal therapies for conditions like endometriosis or PCOS
-
Counseling for relationship and emotional challenges
-
Surgical interventions, if necessary
-
Support groups for chronic conditions or fertility issues
Many hospitals and clinics offer reproductive health services regardless of gender, and seeking help is a sign of strength—not weakness.
Final Thoughts: Protecting Reproductive Health is a Shared Responsibility
Reproductive health is not just a women’s issue—it affects everyone. Conditions like HPV, STIs, infertility, and chronic pelvic disorders remind us that both men and women play a role in prevention, early detection, and care. The good news is that most reproductive health issues are manageable—and often preventable—with the right knowledge and habits.
Education, communication, and routine care are the building blocks of a healthy reproductive system. Don’t wait for symptoms to become severe—take proactive steps to safeguard your health today.
Sources: