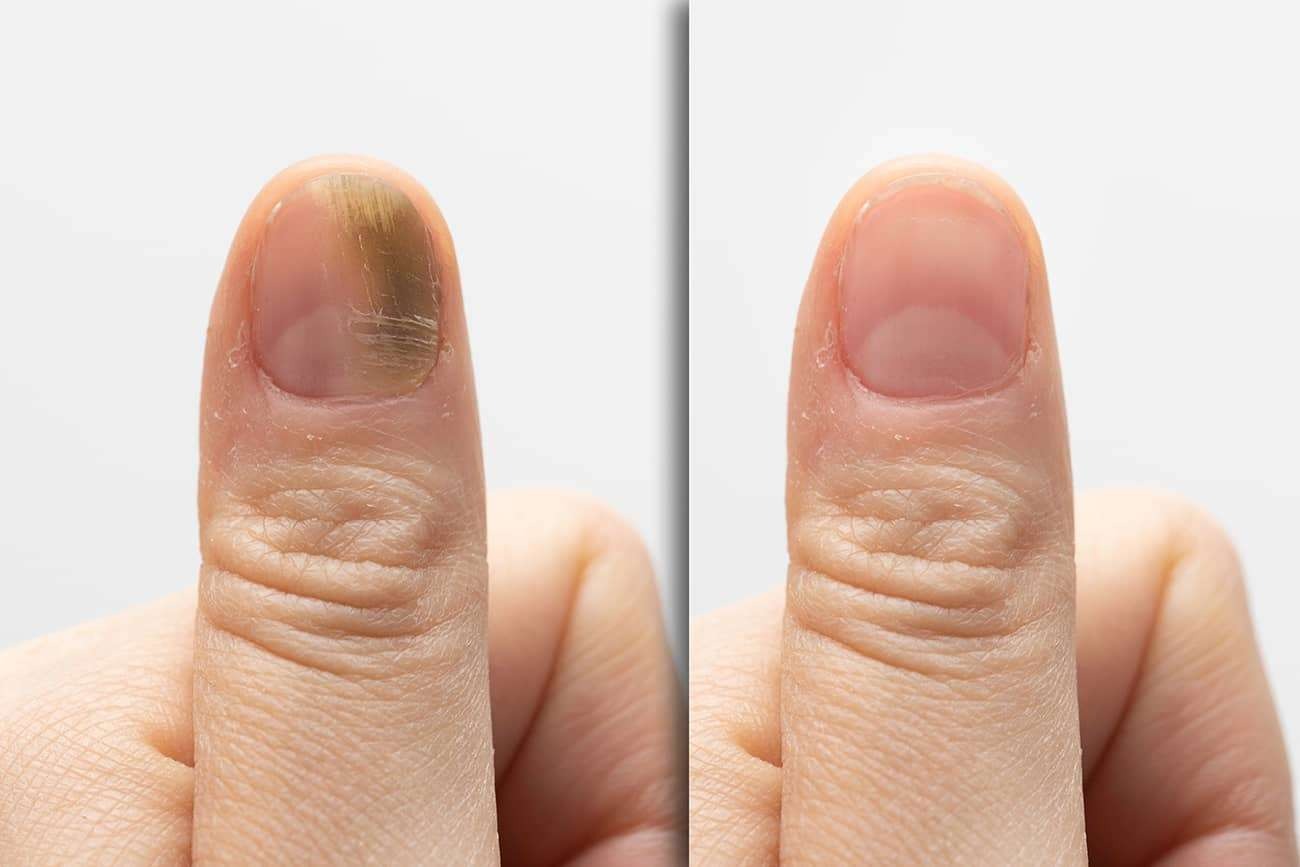
Fungal nail infections, medically known as onychomycosis or tinea unguium, are common conditions caused by fungi that thrive in warm, moist environments. These infections affect the fingernails or toenails and can cause a variety of symptoms that may worsen over time if left untreated.
Understanding the causes, signs, risk factors, and treatment options can help you manage this condition effectively and prevent complications.
What Is a Fungal Nail Infection?

Fungal nail infections occur when fungi invade the nail bed, the nail plate, or the surrounding skin. Fungi are naturally present on the skin and in the environment, but an overgrowth leads to infection.
The same types of fungi responsible for other skin infections—like athlete’s foot, jock itch, and ringworm—can infect the nails. Infection often develops slowly, and initial changes to the nail might be subtle.
Causes and Risk Factors

Fungal infections develop when fungi enter through tiny cracks or breaks in the nail or surrounding skin. These microorganisms thrive in warm, damp environments, making toenails more susceptible since feet are often confined in shoes.
You’re more likely to develop fungal nail infections if you:
-
Have diabetes or a disease that impairs circulation
-
Are over 65 years old
-
Wear artificial nails or use nail polish frequently
-
Swim or frequent public pools and locker rooms
-
Have experienced nail injuries or skin injuries around the nails
-
Keep fingers or toes moist for long periods
-
Have a weakened immune system
-
Frequently wear closed-toe shoes such as sneakers or boots
Men tend to develop fungal nail infections more often than women, and adults are more frequently affected than children. Family history also increases your susceptibility.
Older adults have slower nail growth and may have reduced circulation, making infections harder to clear.
Recognizing the Symptoms

Fungal nail infections may affect part of the nail, the entire nail, or multiple nails. Signs and symptoms to watch for include:
-
Nail thickening or distortion
-
Discoloration—often white, yellow, or brown spots or streaks
-
Brittle, crumbly, or ragged nails
-
Nail lifting from the nail bed
-
Unpleasant odor emanating from the infected nail
-
Surrounding skin redness or swelling (in some cases)
Types of Fungal Nail Infections
-
Distal Subungual Onychomycosis (DSO)
The most common type, usually affecting toenails. The infection starts at the tip of the nail and progresses inward, causing white or yellow streaks and jagged edges. -
White Superficial Onychomycosis (WSO)
This affects the top layers of the nail, creating well-defined white spots that can spread over the nail surface, causing roughness and brittleness. -
Proximal Subungual Onychomycosis (PSO)
Less common, with yellow spots appearing near the cuticle and spreading upward. More frequent in immunocompromised individuals. -
Candida Infection
Caused by yeast fungi, often affecting fingernails, especially in people whose hands are frequently wet. The infection begins around the cuticle, causing redness, swelling, and tenderness.
Diagnosis: Why See a Doctor?
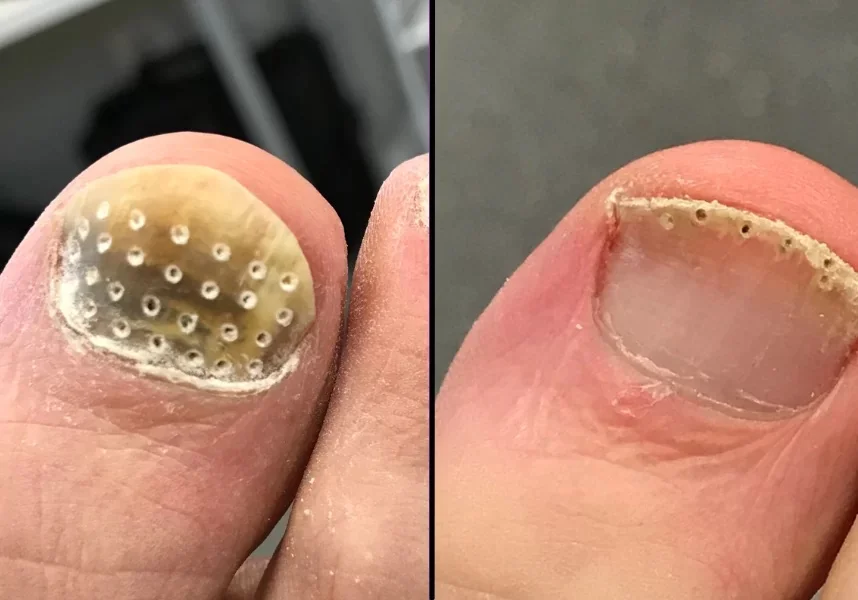
Because other conditions (like psoriasis or trauma) can mimic fungal nail infections, it’s important to get an accurate diagnosis. Your healthcare provider will:
-
Examine the affected nail(s)
-
Take nail scrapings or clippings for microscopic analysis
-
Possibly send samples to a lab to identify the specific fungus
This ensures you receive the appropriate treatment, as some fungal infections respond differently to medications.
Treatment Options
Over-the-Counter Products
Many OTC antifungal creams or nail lacquers are available but often do not penetrate deeply enough to effectively cure toenail infections. They may help in mild cases or prevent reinfection.
Prescription Oral Antifungals
Medications such as terbinafine or itraconazole are commonly prescribed and are generally more effective, especially for toenail infections. They work by attacking the fungus systemically.
-
Treatment duration typically lasts several months because the nail must grow out completely.
-
Potential side effects and interactions with other medications should be discussed with your doctor.
Topical Prescription Treatments
Antifungal nail lacquers or solutions applied directly to the nail may be used alone for fingernail infections or combined with oral medications.
Challenges in Treatment
Fungal nail infections can be stubborn. Nails grow slowly, and complete cure requires the infected nail to be replaced by healthy nail growth. Even after treatment, infections can recur.
If left untreated, fungal nail infections can:
-
Worsen or spread to other nails or skin
-
Lead to permanent nail damage or loss
-
Increase risk of bacterial infections such as cellulitis, especially in people with diabetes
Preventing Fungal Nail Infections
Simple lifestyle and hygiene practices can reduce your risk:
-
Keep nails clean, dry, and trimmed
-
Avoid injuring skin around nails
-
Use moisture-wicking socks and breathable shoes
-
Wear rubber gloves when hands will be wet for extended times
-
Avoid sharing nail grooming tools; ensure salon tools are sterilized
-
Dry feet thoroughly after bathing, especially between toes
-
Limit use of artificial nails and nail polish
-
Avoid walking barefoot in public places like locker rooms or pools
When to See a Doctor Urgently
Seek medical advice if you:
-
Notice changes in nail color, texture, or thickness lasting more than a few weeks
-
Experience pain, swelling, or redness around nails
-
Have diabetes or a compromised immune system and suspect an infection
Early diagnosis and treatment reduce complications and improve outcomes.
Fungal nail infections are common but manageable conditions. With proper care, hygiene, and medical treatment, most people can restore their nails to health and avoid complications. Don’t ignore persistent nail changes—consult your healthcare provider for diagnosis and personalized treatment.