The human body often signals underlying health issues through visible symptoms. In the image provided, several signs are shown: abdominal pain, nosebleeds, red or bloodshot eyes, and bleeding gums. These symptoms, while not always serious, may indicate the need for medical evaluation, especially when persistent. This article will break down each symptom, explore its potential causes, and reference trustworthy sources to guide readers on when to seek professional care.
1. Abdominal Pain: A Common but Important Symptom
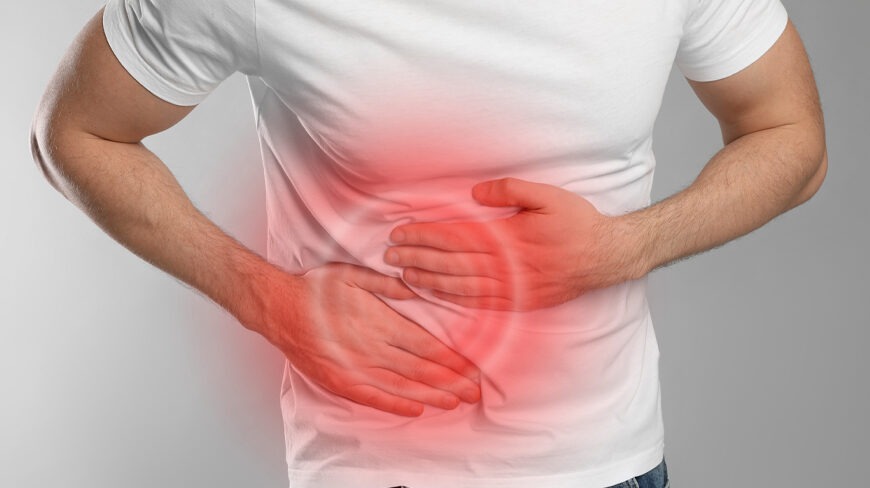
The image shows a person clutching the lower abdominal area, a sign that can point to various internal issues. Abdominal pain can stem from many causes, ranging from mild gastrointestinal disturbances to more serious conditions.
Possible Causes:
- Indigestion or gas: Common and usually harmless.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A chronic condition that affects the large intestine, leading to cramps, bloating, and altered bowel habits (Mayo Clinic).
- Appendicitis: A serious condition requiring immediate attention, typically presenting with severe pain in the lower right abdomen.
- Gastroenteritis: Infections caused by viruses or bacteria that result in inflammation of the stomach and intestines.
When to Seek Help:
The CDC advises seeking medical attention if abdominal pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by fever, vomiting, or bleeding. Persistent discomfort should never be ignored.

2. Nosebleeds (Epistaxis): Often Harmless, Occasionally Concerning
Another image shows a man experiencing a nosebleed. While nosebleeds are common and usually not serious, recurring or heavy episodes may require evaluation.
Common Causes:
- Dry air or allergies: According to the American Academy of Otolaryngology, dry nasal passages are the most common reason for nosebleeds.
- Nasal trauma: Blowing the nose too hard or injury to the nose can rupture blood vessels.
- High blood pressure: Chronic hypertension can increase the likelihood of nosebleeds in some individuals.
- Blood clotting disorders or certain medications (like blood thinners).
When to Seek Medical Attention:
The Mayo Clinic recommends seeing a doctor if nosebleeds are frequent, last more than 20 minutes, or occur after an injury. Recurrent nosebleeds could indicate an underlying health issue, such as a bleeding disorder or uncontrolled hypertension.

3. Bloodshot or Red Eyes: Symptoms of Local or Systemic Issues
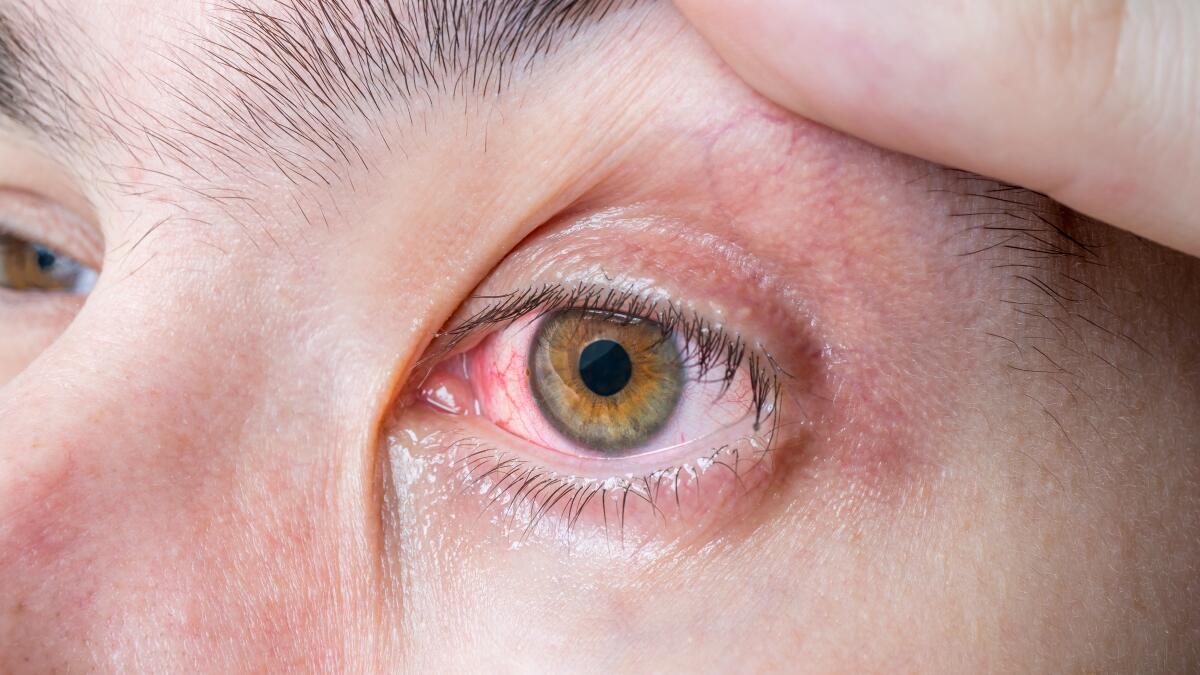
The image includes an eye with significant redness, suggesting irritation or inflammation. A bloodshot eye is typically caused by the dilation of tiny blood vessels on the surface of the eye.
Potential Causes:
- Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye): An infection or allergy-induced inflammation of the conjunctiva, highly contagious and uncomfortable (CDC).
- Eye strain or dryness: Common from prolonged screen time or contact lens use.
- Subconjunctival hemorrhage: A small bleed under the surface of the eye, often harmless and resolving on its own.
- Glaucoma or uveitis: More serious conditions that cause red eyes and can lead to vision loss if not treated.
When to Be Concerned:
If redness is accompanied by pain, vision changes, or discharge, seek medical care promptly. According to WebMD and American Academy of Ophthalmology, symptoms like sudden vision loss or severe discomfort may indicate an emergency.
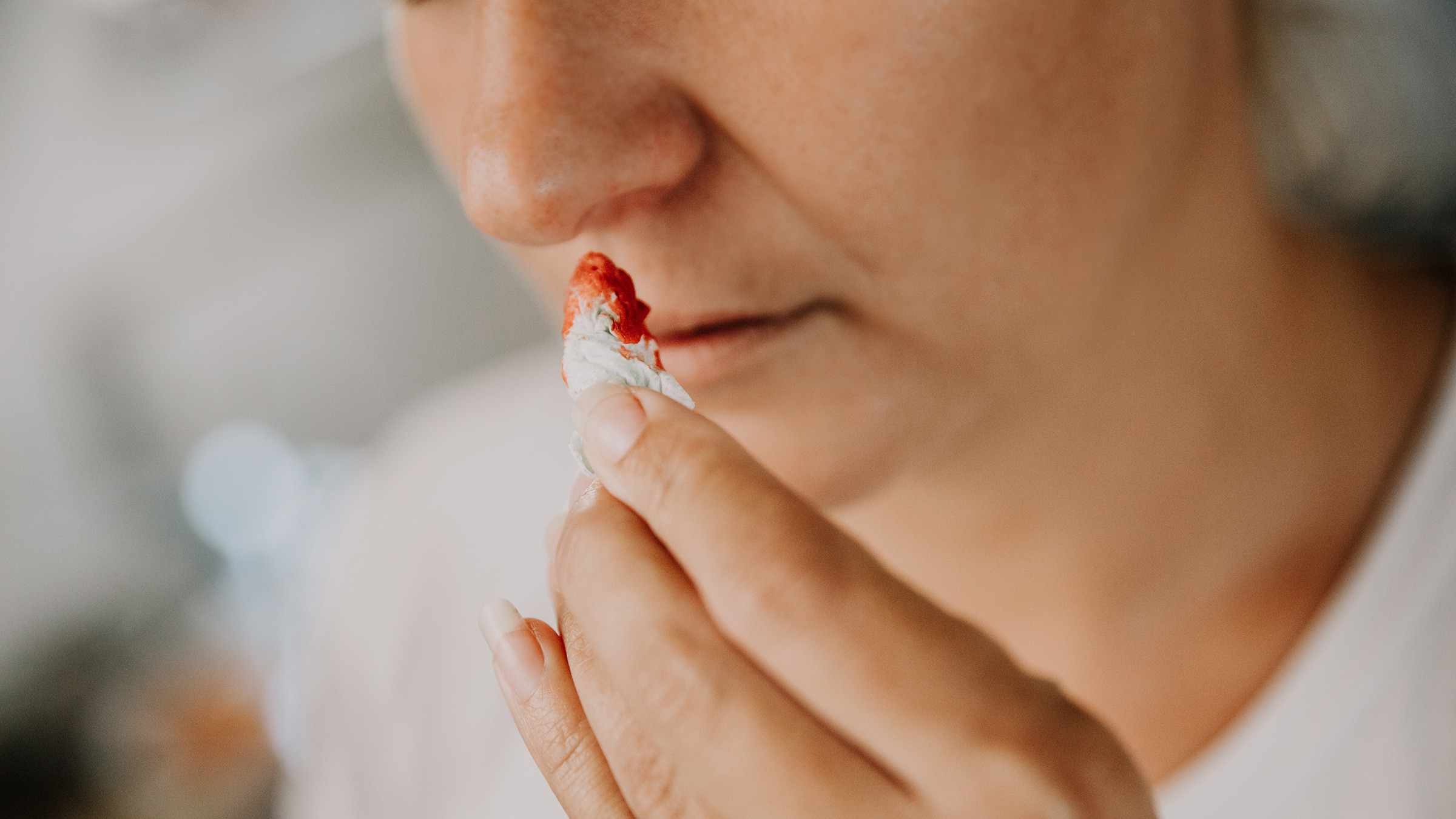
4. Bleeding Gums: A Possible Indicator of Gum Disease or Nutrient Deficiency
The image of bleeding gums when touched suggests oral health issues that may require a dental evaluation. Healthy gums should not bleed during brushing or flossing.
Most Common Causes:
- Gingivitis: The earliest stage of gum disease, caused by plaque buildup. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and bleeding.
- Poor oral hygiene: Infrequent brushing or flossing can lead to inflammation.
- Vitamin C deficiency: A lack of this essential nutrient can lead to bleeding gums, a condition known historically as scurvy (World Health Organization).
- Use of anticoagulants: Medications that affect blood clotting may lead to increased gum bleeding.
What to Do:
The American Dental Association (ADA) advises regular dental visits and brushing twice daily to prevent gum disease. If bleeding persists, a dentist can assess for periodontitis or other conditions.

Trusted Medical Sources for Further Reading
For individuals seeking more information on the topics covered above, the following authoritative websites provide accurate, up-to-date health content:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Mayo Clinic
- American Dental Association (ADA)
- American Academy of Ophthalmology
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- National Institutes of Health (NIH)
These organizations offer free resources for understanding symptoms, accessing care, and maintaining overall wellness.
Conclusion
Symptoms like those illustrated in the image—though common—should not be ignored if they persist or worsen. Abdominal pain, nosebleeds, red eyes, and bleeding gums may indicate conditions ranging from mild to serious. The key is to monitor symptoms carefully and consult qualified healthcare professionals rather than rely on speculation or misinformation.
By prioritizing health literacy and evidence-based care, individuals can make informed decisions and protect their long-term well-being.