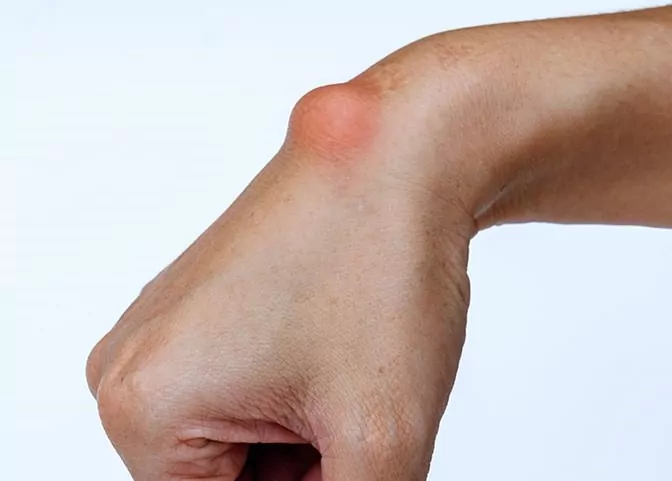
A wrist ganglion, also known as a synovial cyst, is a common condition where a fluid-filled lump develops near a joint or tendon, often on the back or front of the wrist. While ganglion cysts are typically harmless, they can sometimes cause discomfort, pain, or limited mobility. In this article, we explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for wrist ganglion cysts to help you manage the condition effectively.
What Causes a Wrist Ganglion Cyst?

A wrist ganglion forms when synovial fluid, which naturally lubricates the joints and tendons, accumulates in an abnormal sac or capsule. Although the exact cause is not always clear, several factors are known to increase the risk of developing a ganglion cyst:
1. Repetitive Wrist Movements
Regular activities that put strain on the wrist, such as typing, writing, or engaging in certain sports, can stress the wrist joint and increase the likelihood of cyst formation. The repetitive movement can contribute to the accumulation of synovial fluid, leading to the development of a ganglion.
2. Previous Wrist Injuries
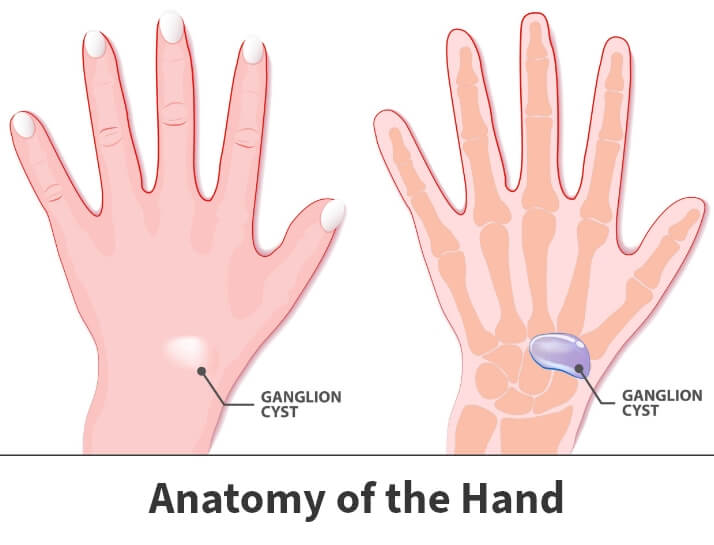
Trauma to the wrist, such as a sprain, strain, or fracture, can trigger the formation of a ganglion cyst. Injuries may cause damage to the synovial lining of the joint, which can lead to fluid buildup and cyst formation.
3. Arthritis
Certain types of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis, which involves joint inflammation, can contribute to the development of ganglion cysts. The inflammation can disrupt normal joint function, creating an environment that promotes cyst formation.
4. Genetic Factors
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing ganglion cysts. This means that people with a family history of ganglion cysts may be more likely to develop them.
Source:
Common Symptoms of a Wrist Ganglion
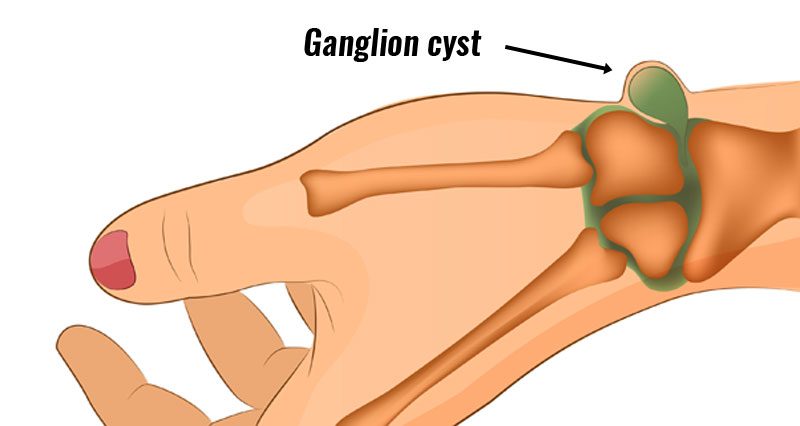
Ganglion cysts can vary in size and consistency, and they may grow or shrink over time. Symptoms can differ depending on the size and location of the cyst, but common signs include:
-
A Visible Lump: The most obvious symptom is a soft lump or swelling that appears on the wrist, often near a joint or tendon.
-
Pain or Discomfort: Some people experience pain or tenderness, especially when moving the wrist or applying pressure to the cyst.
-
Pressure or Numbness: In certain cases, the cyst may press against nearby nerves, causing a sensation of pressure, numbness, or tingling.
-
Reduced Mobility: In more severe cases, a ganglion cyst may restrict wrist movement, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks.
Source:
Treatment Options for Wrist Ganglions
The treatment for a wrist ganglion depends on its size, symptoms, and impact on daily life. Below are some common treatment options:
1. Observation (Watch and Wait Approach)
If the cyst is small, painless, and does not affect wrist function, doctors may recommend simply monitoring it. Many ganglion cysts resolve on their own without the need for intervention. This approach is most suitable for cysts that do not cause significant symptoms or discomfort.
2. Immobilization

Wearing a wrist brace or splint can help reduce pressure on the joint, preventing the cyst from growing and alleviating any discomfort. Immobilization can also provide temporary relief for those experiencing pain from the cyst.
3. Aspiration (Draining the Fluid)
Aspiration is a non-surgical procedure in which a doctor uses a needle to drain the fluid from the ganglion cyst. While this can offer temporary relief, it is not a permanent solution. The cyst sac may remain intact, and the cyst can return over time.
4. Surgical Removal (Ganglion Excision)
If the ganglion causes persistent pain, limits wrist movement, or recurs after aspiration, surgical removal may be the most effective option. The surgery involves excising the entire cyst sac, which reduces the likelihood of the cyst returning. Surgical treatment is often recommended for large or symptomatic cysts.
Source:
When to See a Doctor

Ganglion cysts are usually benign and don’t pose a major health risk. However, you should consult a doctor if:
-
The cyst grows rapidly or changes in texture.
-
You experience persistent pain or discomfort.
-
The cyst causes numbness, tingling, or weakness in your wrist or fingers.
-
Wrist movement becomes restricted, affecting daily activities.
A healthcare professional can provide a diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate treatment based on the cyst’s size and severity.
Source:
Final Thoughts: Managing Wrist Ganglion Cysts
Wrist ganglion cysts are generally benign and often resolve on their own. However, if the cyst causes discomfort or limits your wrist mobility, several treatment options are available. Non-invasive treatments such as bracing and aspiration can provide relief, while surgical removal may be necessary for more severe cases.
If you notice any changes in the appearance or symptoms of a ganglion cyst, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.