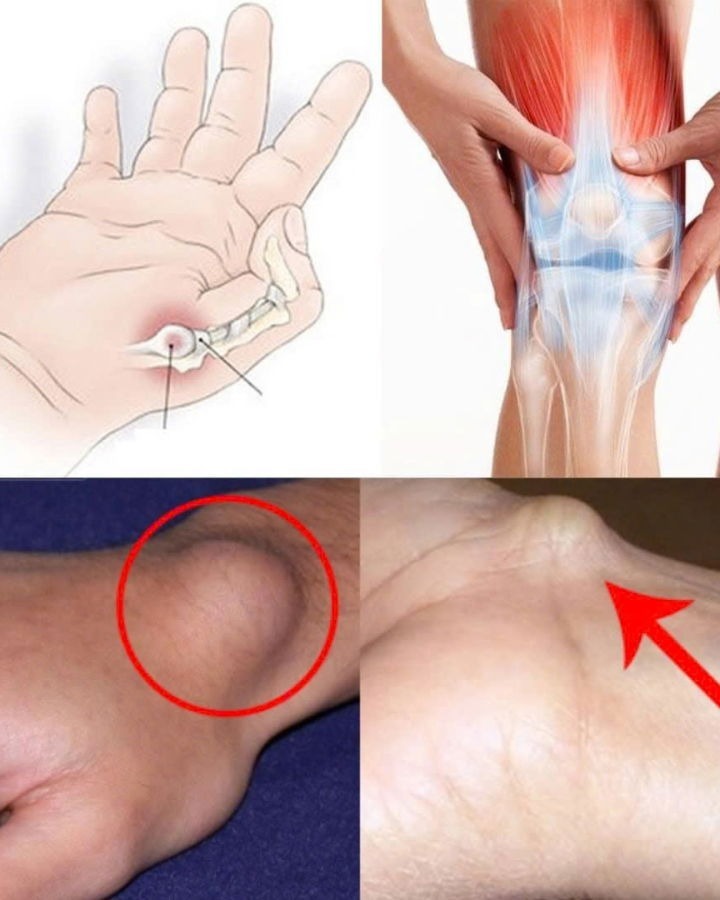
Finding a small lump beneath your skin, whether on your wrist or foot, can be a cause for concern. While it’s natural to feel uneasy, it’s important not to panic. The bump you notice might be a cyst, a common occurrence that’s usually harmless. Let’s take a closer look at what cysts are, when they should be a cause for concern, and the best steps to take if you find one.
What is a Cyst?

A cyst is a small sac or lump that forms under the skin, filled with fluid or a thicker substance. While the term “cyst” may sound alarming, these lumps are often benign and not something to immediately worry about. Cysts can appear in various parts of the body, and they vary in size, but most don’t cause pain or pose any real threat to your health.
The Common Types of Cysts
Cysts are categorized based on their location and the substance they contain. The most common types of cysts include:
Skin Cysts
Sebaceous cysts (or epidermoid cysts) are typically small, round lumps that form just under the skin. These cysts are usually harmless, often painless, and tend to be filled with a thick, oily substance. In many cases, sebaceous cysts do not require treatment unless they cause discomfort, become inflamed, or grow in size.
Synovial Cysts
Synovial cysts are typically found near joints such as the wrist, knee, foot, or hip. These cysts can develop due to repetitive motion or joint injury. In some cases, synovial cysts might disappear on their own over time. However, if they become painful, inflamed, or bothersome, a minor surgical procedure may be recommended to remove them.
When Should You Be Concerned?
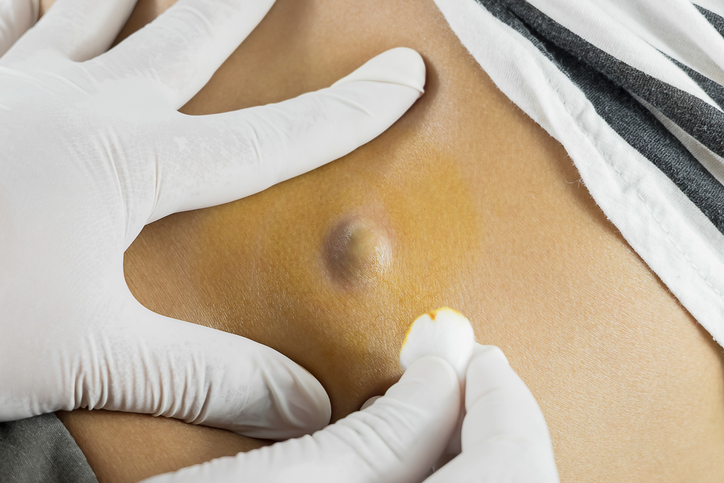
It’s common to feel anxious when discovering a lump on your body. However, most cysts are non-cancerous and harmless. Even so, there are certain signs that you should not ignore. If a cyst shows any of the following symptoms, it may indicate an underlying problem, and you should consult a healthcare professional immediately:
-
Redness and swelling: This could indicate an infection.
-
Pain or tenderness: A cyst that becomes painful or tender might be infected or inflamed.
-
Fever: If you have a mild fever along with a cyst, it might be a sign of an infection.
-
Rapid growth: If the cyst grows quickly or changes shape, it could be an indication that it’s not just a simple cyst.
-
Difficulty moving: If the cyst is located near a joint and affects movement, it may require medical intervention.
What to Do If You Find a Cyst
The first thing to do if you discover a lump under your skin is not to panic. Instead, take the following steps:
-
Don’t Squeeze or Pop: Avoid squeezing or trying to pop the cyst, as this could lead to infection or worsen the condition.
-
Monitor the Cyst: If the cyst is small, painless, and doesn’t change over time, it’s likely harmless. Keep an eye on it, and note any changes.
-
Seek Medical Advice: If the cyst becomes painful, inflamed, or shows signs of infection, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. A doctor or dermatologist can provide a diagnosis and suggest treatment options.
How Can Cysts Be Treated?

Treatment for cysts depends on the type of cyst and the severity of symptoms. The majority of cysts do not require aggressive treatment and may resolve on their own. However, in some cases, treatment may be necessary:
-
Drainage: If the cyst becomes large, painful, or infected, a doctor might drain it using a needle or incision.
-
Surgical Removal: For persistent or bothersome cysts, surgical removal may be recommended. This procedure is usually done on an outpatient basis and has minimal recovery time.
-
Medication: In cases of infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection before further treatment is carried out.
Preventing Cysts: Tips for Healthier Skin

While not all cysts can be prevented, there are some steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing them:
-
Maintain Good Hygiene: Keep your skin clean and avoid squeezing or irritating any bumps that appear on your skin.
-
Avoid Trauma: Try to avoid injury or repetitive motion in areas that are prone to cysts, such as the wrist or knee.
-
Moisturize Your Skin: Keeping your skin well-moisturized can help prevent irritation that could lead to cyst formation.
-
Wear Proper Protection: If you are involved in activities that involve repetitive motion, consider wearing protective gear to reduce the risk of joint-related cysts.
-
Eat a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet with vitamins and minerals supports overall skin health and can reduce the likelihood of developing skin-related conditions, including cysts.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If the cyst becomes painful, inflamed, or changes in appearance, you should seek medical advice. A dermatologist can help determine whether it’s a simple cyst or something that requires further treatment. In general, if the cyst is:
-
Painful or tender to the touch
-
Rapidly growing in size
-
Associated with redness, swelling, or fever
-
Affecting your movement or function, especially if located near a joint
It’s always best to have it checked by a healthcare professional to ensure it’s not something more serious.
Conclusion: Cysts Are Common, But Knowing When to Seek Help Is Key
Cysts are a common occurrence, and most of the time, they are not a cause for concern. Whether it’s a sebaceous cyst on your skin or a synovial cyst near a joint, they are usually harmless and don’t require immediate treatment. However, if the cyst shows signs of infection or other concerning symptoms, it’s important to consult a doctor or dermatologist.
By staying vigilant and seeking timely medical advice, you can ensure that any cysts you encounter are addressed effectively, preventing complications and ensuring your peace of mind. Remember, while most cysts are non-cancerous, early detection and treatment are essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Sources:
-
American Academy of Dermatology – Cyst Diagnosis and Treatment: aad.org
-
Mayo Clinic – Cyst Overview: mayoclinic.org
-
WebMD – Synovial Cysts: webmd.com