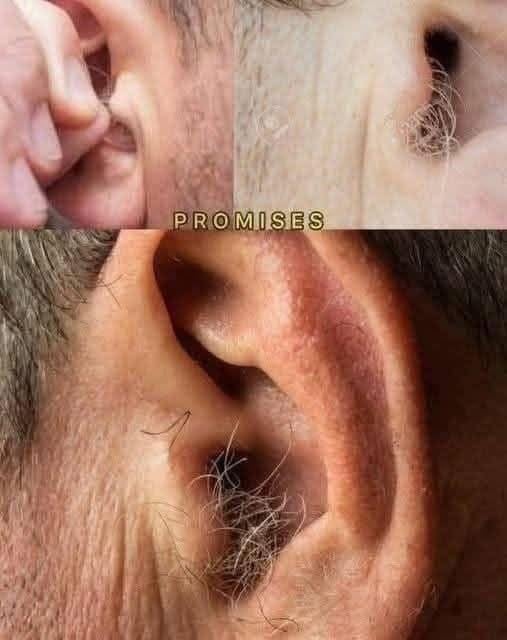
Introduction to Ear Hair: A Normal Part of the Human Body
Many people are surprised the first time they notice hair on or inside their ears. While it may seem unusual, ear hair is actually quite normal and common. The human body is mostly covered in some form of hair, except for areas like the palms, soles, and lips. Ear hair, just like other body hair, serves important functions even though for some it becomes more noticeable with age.
If you have ever wondered why ear hair grows or what you can do about it, this article provides a comprehensive explanation of causes, the role of ear hair, its health implications, and safe ways to manage it.
Why Ear Hair Exists and Its Functions
.jpg?rev=653e41654a284a4d9ba5fdb1a3c2d727)
Ear hair exists in two main locations: on the outer ear (the visible parts around the ear canal) and inside the ear canal itself. Each serves distinct purposes:
-
Protective Function: Hair inside the ear canal works alongside earwax to create a barrier against dust, dirt, and small particles, helping to prevent them from reaching the sensitive eardrum.
-
Sensory Function: Deep inside the ear, tiny hair-like structures detect fluid movement in the inner ear, essential for hearing and balance.
-
Evolutionary Remnant: Like most body hair, ear hair is part of an evolutionary heritage. While less important than before, it has persisted as a natural feature of humans.
Interestingly, even before birth, humans develop soft, fine hair called lanugo that covers the entire body, including the ears. This usually disappears shortly after birth, but some babies—especially those born prematurely—can retain it longer.
Why Ear Hair Becomes More Noticeable with Age

For many individuals, ear hair becomes more prominent as they get older. This is largely due to hormonal changes that cause hair follicles in certain areas to grow longer or thicker. Particularly in men, increased levels of androgens (male hormones) can stimulate hair growth in the ears and nose.
This natural process is normally harmless, though it can sometimes be aesthetically concerning for some people.
Safe Methods to Manage Ear Hair
If ear hair becomes bothersome, there are safe ways to groom and reduce its appearance:
-
Trimming: The preferred and safest option is to use an electric trimmer designed specifically for ear and nose hair. These devices trim hair without cutting or damaging the skin.
-
Waxing: This method can remove outer ear hair temporarily and can reduce growth over time but should be performed by professionals to avoid irritation or injury.
-
Laser Hair Removal: For longer-lasting results, laser treatments offered by certified technicians can effectively reduce ear hair with minimal discomfort.
-
Avoid Unsafe Practices: Do not use scissors, plucking, or chemical hair removers directly inside the ear canal to avoid injury, infection, or damage to sensitive ear structures.
When to Seek Medical Advice

Ear hair generally does not cause health issues, but if you notice sudden or excessive hair growth coupled with other symptoms like itching, hearing problems, or discomfort, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. Underlying conditions or hormonal imbalances may occasionally contribute to excessive hair growth.
Conclusion
Ear hair is a normal and functional part of the human body that plays protective and sensory roles. While it may become more prominent with age, it usually does not signal health problems. Safe grooming methods allow individuals to manage ear hair without risk.
Understanding the nature and role of ear hair helps normalize this common occurrence and promotes informed care.